Quick facts about The Merge…
-
Ethereum 2.0 is the transition from the proof of work (PoW) consensus mechanism to the proof of stake (PoS) model.
-
PoW is used by a handful of blockchains, the most notable of which is the father of cryptocurrencies—Bitcoin (BTC). Ethereum also started out using the PoW method, but as its popularity grew, PoW was found to be too labour intensive for Web 3.0, too slow, and too environmentally unfriendly.
-
PoS on the other hand completes transactions more efficiently, uses less power, and benefits from much lower transaction fees.
-
Network stakeholders validate transactions and are rewarded for their efforts with the native currency of the platform—in this case, ETH.
Why do people call The Merge Ethereum 2.0?
Ethereum 2.0, Eth2 or The Merge are all the same thing under different names. While Ethereum tried to distance itself from the first label it gave its new project—Ethereum 2.0—for most people with more than a passing interest in the project, the name has stuck.
To solve the problem of confusion caused by shifting semantics from the world’s leading smart contract blockchain, the terms Ethereum 2.0, Eth2, and The Merge will be used interchangeably throughout this deep dive into the topic.
What is Ethereum 2.0?
The ETH Merge is the transition from Eth 1 to Eth2. The Merge involves the fusion of the Beacon chain, layer 1 PoS testnet with Ethereum’s PoW mainnet. For a time the two have been running in parallel to avoid a platform meltdown in the event of a sudden switch. When the PoS consensus mechanism replaces the current PoW consensus mechanism, The Merge will be complete and PoW will no longer exist on the Ethereum blockchain.
The Merge aims to solve a number of problems that have long hampered Ethereum and its use cases. These are:
-
Congestion
-
High gas fees
-
Security challenges
-
Speed of transactions
-
Scalability
This article aims to answer each and every question you might have about how the team at Ethereum plan to tackle these issues and assess the company’s roadmap.
What is the difference between ETH 1.0 and ETH 2.0?
Ethereum 1.0, or Eth1, is the place where Ethereum’s smart contracts are signed and sealed. These are currently handled by a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus similar to Bitcoin, which the Ethereum team wants to move away from.
Eth2 aims to flip PoW to Proof of Stake (PoS). This PoS layer didn’t exist before which meant that Ethereum’s layer 1 had to do all of the hard data processing. This was slow and caused bottlenecks and other inefficiencies.
With the PoS consensus layer in place, Ethereum 2.0 will be able to process and execute smart contracts more quickly. The Merge refers to the fusion of these existing and new layers—what is known as a hard fork—that gets rid of the old PoW consensus mechanism and ushers in Proof of Stake.
What is a consensus mechanism and how does it work?
Consensus mechanisms are simply a way for computers working together to confirm that an event happened. If there are enough validator nodes on the network, these cross-check information with one another to agree on the ‘truth’ of an event. If more than 51% of validator nodes agree with each other then ‘consensus’ has been reached.
This is a vital process in distributed databases and smart contracts which make decisions algorithmically. The computers are effectively witnesses that agree or disagree that a consensus is reached. This also prevents bad actors from taking over the network in a biased way.
Proof of work (PoS) vs proof of stake (PoW)
In its most simple form, Proof of Work (PoW) is where computers do ‘the work’ solving complex cryptography problems to gain a reward. It’s a bit like sending a robot down into a pit to mine gold. Only the best, most efficient and hard-working robots will bring back the gold deposits. Bitcoin is the number one example of a PoW consensus mechanism where powerful computers work ever harder to mine the next coin.
Proof of Stake (PoS) is reliant on cooperation between people who use their computers to validate transactions. To be allowed to do this—in other words, to be accepted as a validator—participants must stake the blockchain’s native cryptocurrency (in the case of Ethereum 2.0 this is ETH), to earn the rewards. Of relevance now, PoW is maligned by environmentalists because of the huge amount of computational power, and therefore energy, required for the crypto puzzles to be solved. PoS, on the other hand, uses far less energy to achieve a similar goal.
What are the four phases of The Merge?
There are four phases to the full rollout of Ethereum 2.0. Below is a quick run-through of what happens in each phase:
Phase 0: In December 2020, Phase 0 marked the launch of the PoS consensus mechanism named Beacon. Running in parallel to Ethereum’s PoW mainnet, Beacon is made up of PoS validators with staked ETH to ensure that all of the shards that enable Eth2 to scale are synchronously working.
Phase 1: This is where the shard chains start actively working. If phase 0 is akin to starting the engine of a car, Phase 2 is putting the foot on the gas and road testing the tech. Each shard is a PoS blockchain working both independently and in conjunction with the other shards to process all transactions.
Phase 1.5: This is where the PoW Ethereum chain, or mainnet, is ‘merged’ with the new PoS Ethereum chain. This is the main transition from the legacy system of processing transactions to the new system.
Phase 2: At this point, all shards are active. At this point, The Merge will be complete with all shards communicating with one another, efficiently running smart contracts and weeding out bad actors.
Why is The Merge happening now?
Although the Merge is happening now, this is something that has been at the forefront of Ethereum founder, Vitalik Buterin’s, mind for a long time. Aware of the high energy usage required for PoW consensus mechanisms and the related congestion issues, Buterin’s desire to improve the infrastructure and make Ethereum more scalable, sustainable, secure and much faster has existed for almost as long as Ethereum itself.
The lack of progress and constant delays, however, led to some of Buterin’s colleagues and co-founders jumping ship and setting up new layer one protocols, namely Cardano (Charles Hoskinson), and Polkadot (Dr Gavin Wood).
When will Ethereum 2.0 happen?
The Merge is likely to happen sometime in 2022, though many experts believe this could happen later.
Why is the move to Eth2 taking so long?
To prepare for the move to PoS, a consensus layer had to be built to run in tandem with the mainnet where dApps and smart contracts live. In essence, this was like creating Ethereum all over again in a different way. Moving thousands of dApps from one system to another is also no easy feat.
The team decided to build a parallel chain rather than simply switch from PoW to PoS to reduce the risk of breaking the network and taking thousands of dApps built on the network down at the same time.
Will Ethereum be a different coin after The Merge?
No, the only thing that will be different is basically what’s under the hood. The token will be exactly the same. However, the tokenomics of Eth2 will differ in that the ecosystem will become deflationary. This means that fewer ETH will be available, which is positive for the price of ETH and good news for holders of the coin.
What are the improvements of The Merge?
The improvements of The Merge are happening specifically on the consensus layer. This is where validations take place. Currently, miners validate blocks through PoS. This requires massive amounts of computer power and uses up a lot of energy. This is not a good thing when the world is trying to reduce its carbon footprint.
Ethereum moving to proof of stake will decrease energy consumption by 99.9%. To put this in perspective, this is roughly the same amount of electricity that gets used by the entire population of Mexico each year—around 300 terawatt-hours!
As previously mentioned, after The Merge, Ethereum will also provide a better user experience by running more efficiently.
How is the new Ethereum PoS chain secured?
The new chain forming the backbone of Ethereum 2.0 is secured by validators. These are pools of individuals who stake their Ethereum to earn rewards in ETH. Their stake and, therefore, their presence helps secure the network. Think of staked ETH a bit like you would fuel in a car.
Currently, there are around 10million ETH deposited with an estimated value of almost $30billion. Packaged into blocks of 32 ETH. It is these deposits that provide validation nodes on the Ethereum Beacon Chain.
How can I stake Ethereum and become a validator to earn rewards?
The hardware costs, setup and initial amount required to become a validator are onerous for anyone without experience—or enough capital.
For example, just to become a validator you need to be able to stake a minimum of 32 ETH which is the best part of $100k at the time of writing. The good news is that you can leapfrog this hassle by heading to an exchange that supports staking Ethereum. Below are some of the best exchanges where you can buy Ethereum and stake it.
Will the cost of transactions on Ethereum go down with The Merge?
No. This is a common misconception that needs to be debunked. There are five layers in blockchain architecture. These are:
-
Hardware layer
-
Data layer
-
Network layer
-
Consensus Layer
-
Application and presentation layer, also known as the execution layer
All of the changes are being made to the consensus layer where validations take place. Although this will ease congestion and speed things up, transactions are finalised in the execution layer which remains unchanged.
The good news is the reduction in congestion should reduce price volatility, which will be welcome news for those who transact regularly on Ethereum. But for people who want to move small amounts of crypto around on Ethereum’s platform after The Merge, it will still remain a relatively expensive option compared to other layer one blockchains such as Solana.
How will Ethereum 2.0 affect the price?
The future price of any cryptocurrency is notoriously difficult to predict, and Ethereum is no exception. This is because there are so many variables at play, from government regulations to wider fundamentals such as inflation and geopolitical uncertainty.
That said, it is widely believed among experts, based on institutional behaviour and the high amount of total value locked (TVL) by stakeholders in the network—combined with more favourable tokenomics—that price appreciation is likely.
Many expect Ethereum’s transition to PoS will be positive for the price of the coin with experts suggesting that the price of Ethereum after The Merge could breach the $10,000 mark—more than 3X its current price. For a more detailed breakdown of possible price outcomes over the coming years see below.
Five-year price prediction for Ethereum (ETH) after The Merge?
Despite a multitude of spikes and dips typical of the volatile cryptocurrency markets, if you zoom out on Ethereum, you could argue that it has been on a momentous bull run since it was created.
In 2015, you could buy one ETH for just $0.31. By the end of 2021, the same coin would have cost more than $4500. In percentage terms, that’s over a 1.4million percent increase in just 7 years!
Experts now predict that Ethereum could reach $10,000 or more in 2022 and beyond. At CoinText, we like to take a more conservative view, and while we do see ETH hitting $10,000, we don’t think that will happen before 2026.
Below are some estimates of price predictions for Ethereum in the next five years, based on our technical analysis.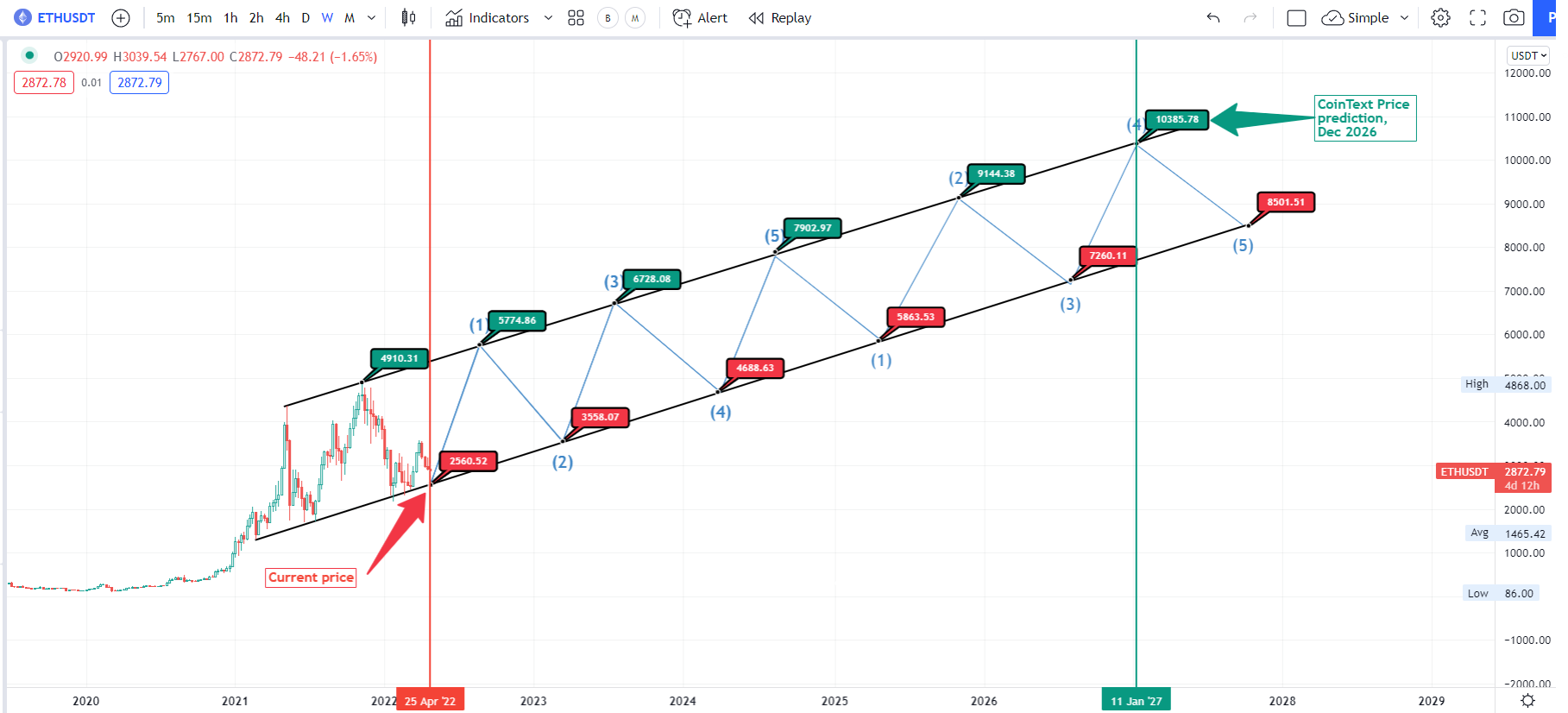
Ethereum price 2022 (high/low): $2171 / $ 5774
Ethereum price 2023 (high/low): $3558 / $6728
Ethereum price 2024 (high/low): $4688 / $7902
Ethereum price 2025 (high/low): $5863 / $9144
Ethereum price 2026 (high/low): $7260 / $10,385
What will the future be for Ethereum 2.0?
Once Ethereum 2.0 is in place, the increased speed of the network will be a boost to Web3 developers keen to build dApps on Ethereum’s infrastructure.
What are the risks with The Merge?
The main risks associated with The Merge are linked to its competition. While Ethereum has a first-mover advantage in the layer one blockchain space, it has had to learn from its own mistakes. These include glaring security problems resulting in hacks and many delays in upgrades and forks that caused frustration among the community.
Perhaps the biggest problem the blockchain has had in the past is seeing some of its co-founders and leading developers jump ship to start (or attempt to start) brighter and shinier versions of Ethereum. Other so-called ‘Ethereum Killers’ have appeared, such as Solana and Avalanche, wielding their virtual axes ready to cut Ethereum down to size.
So, the real risk for Ethereum is speed. For Ethereum 2.0, plagued by delays, the question is: can it achieve The Merge and successfully transition to PoS before new layer 1 platforms either steal or lure new developers away by promising, and delivering, better Web3 solutions.
What happens to ETH after the merge?
After the Ethereum Merge, shard chains will be implemented.
What is sharding and what are shard chains?
Sharding is technology implemented on blockchains to ease congestion and get rid of bottlenecks. Shards enable greater data throughput and scalability. Ethereum 2.0 will have 64 shards available to process data.
A good way to think of this is as taking a single track road and turning it into a 64 lane highway. This eases congestion and makes the transfer of data much faster.
Will Ethereum 2.0 replace Ethereum?
Yes, Ethereum 2.0, which is Proof of Stake, will replace Ethereum 1.0 which is Proof of Work. But only the consensus mechanism is being replaced. This means that, instead of miners extracting new coins from the Ethereum network and receiving mining rewards, stakers will be rewarded for holding and staking ETH.
The tokenomics of Ethereum will also change with more coins being burned. This is good for the price of ETH. Vitally, the blockchain’s native cryptocurrency, ETH, remains unchanged in The Merge.
Will Ethereum 2.0 have a different crypto coin?
No. Ethereum’s native coin, ETH, will not change. There will be no additional tokens added to the ecosystem either. The only cryptocurrency on Ethereum will still be ETH.
How do I prepare for the Ethereum upgrade?
Unless you want to become a validator and stake ETH to earn rewards, there is nothing you need to do to prepare for the upgrade as Ethereum aims to make the transition as seamless as possible.

