With all the talk about moving towards a digital revolution, where we move away from traditional money and develop ways to bring cryptocurrency and blockchain technology to the mainstream, there is always one issue that rears its head. Many compare the rise in cybercrime with the rise in digital in general, and deem cryptocurrency less safe than, paper money, for example. But how safe is cryptocurrency – and could this doubt be why the mainstream isn’t adopting it as much?
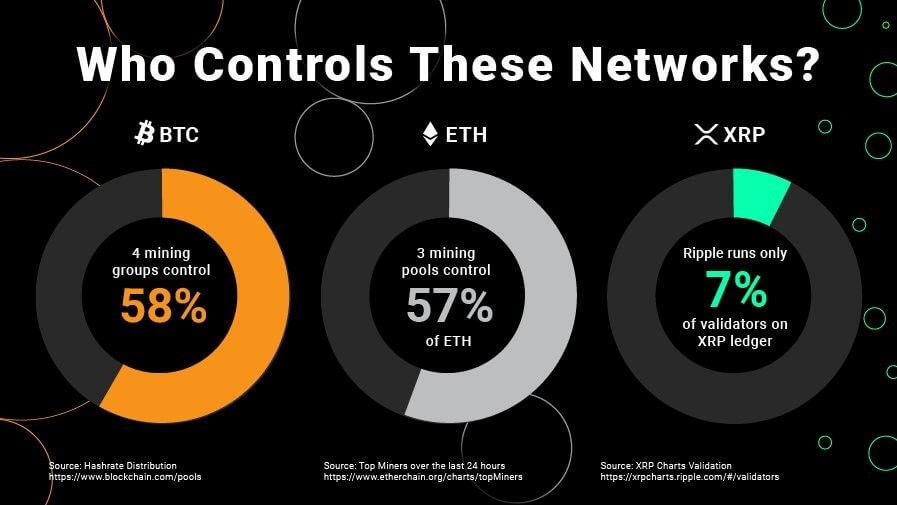
While hackers have gained more notoriety in recent years, and large-scale hacking jobs have afflicted huge companies, it doesn’t necessarily mean that cryptocurrency is less secure from crime than more traditional ways of handling money. The digital coin has many ways in which it can protect itself from hackers. While some blockchains are scurrying to defend their digital wallets, others, such as Ripple (XRP) have built-in defence against hackers. As we identify greater threats to our digital funds, companies are making security their key priority.
How is Ripple Defending Against Hackers?
In the war against hackers, crypto providers need to become proactive in order to defend their assets and protect their customers. While some providers are strengthening their digital wallet services, others are taking a different approach based on how they are built. Blockchain Ripple is defending itself against attackers by the very way it works. Unlike other blockchains, Ripple uses cryptography to protect users, but the nodes that are being protected aren’t individuals but trusted operators on the Ripple network. This means that while Ripple works as efficiently as a traditional blockchain, it works in more of a closed ecosystem that makes the security more efficient and defends against possible hacks. This potential is one of the reasons why investors consider buying XRP to be a good investment.
Kaspersky Lab Reports First Cryptocurrency Hack

Russian internet security firm Kaspersky Lab has reported that North Korean hackers managed to infect a cryptocurrency exchange with malware on both Windows and macOS for the first time, marking a shift in how we view cryptocurrency security. Following the download of a tainted app, the “AppleJeus” virus rooted itself in a crypto exchange. The aim of the malware was to appropriate cryptocurrency funds by the infamous Lazarus Group operating out of North Korea. Security officials noted that not only were fake securities created, but the group went as far as developing the virus across operating systems so the OS wouldn’t be a barrier to their attempted hack.
This Isn’t the First Crypto Related Hack
Earlier in the year, security experts found that Slack and Discord were also being targeted by employees talking about crypto coins, with hackers impersonating key individuals in order to execute the malware. Given how the digital coin world was specifically targeted indicates that the nature of blockchain cryptocurrency could make it more susceptible to theft than traditional money exchanges through bank accounts. But there are ways and means for users of cryptocurrency to protect their digital coin and ensure it stays out of the reach of hackers.
The only reason that figures show cybercrime and hacking are on the rise is that digital in general is on the rise. Crime has always existed and those inclined will always find a way to commit crime, regardless of how digital your money becomes. The rise in hacking is likely due to the rise in digital in general, and likely grows proportionally. Having hacking occur early in the adoption process is beneficial to digital companies, who are able to use it to test the integrity of their systems and their offering. Without small hacking attacks early on, the security would not be able to become as robust as it is in order to protect your digital assets.
Featured image source: Pixabay

