How to Trade Bitcoin in 2025 - Complete Guide
The goal of trading is to benefit from an asset’s price movements in the short-medium term, and this holds true for cryptos like Bitcoin. The flagship crypto is popular for its ability to reach new price peaks.
Trading is how thousands of people around the world capitalise on the unprecedented movement of Bitcoin’s price for profits.
This page dives into how to trade Bitcoin. It explores the differences between trading and investing, how to get started in simple steps, where to trade Bitcoin, and trading strategies.
At the end of this page, you should be able to open a trading account, fund it, create personal trading strategies, and set orders. Note that trading Bitcoin for profit is a journey. You only get better with time and practice.
The Best Bitcoin Exchanges to Use - Our Top 3 Choices
Looking for a quick answer? Here are our top Bitcoin exchanges to use.
Top Bitcoin Exchanges - Key Metrics
The Best Bitcoin Platforms to Use - Why They Made the Cut
The Top Bitcoin Exchanges Reviewed
How to Trade Bitcoin - Quick Guide
To immediately begin trading Bitcoin, you’ll need to first sign up for a broker or exchange.
1. Sign Up with a Broker or Exchange
You’ll need to sign up with a suitable broker or exchange. Ensure that your chosen broker has an industry-standard trading platform that can be used to make predictions and set orders, and are regulated in your region.
Brokers like eToro are a great option as they are fully regulated in various countries and have a good coin selection.
2. Fund Your Account
Once you’ve created your account and completed KYC verification, you’ll need to fund your account. Always note the funding and withdrawal methods supported by your platform. Most brokers support bank cards, electronic wallets like PayPal, and bank transfers.
3. Start Trading
Once your account has funds, navigate to your broker trading terminal. The terminal is an interface with a chart that tracks price movements, indicators that help you predict future price movements, and an order book that places buy and sell orders.
What is Bitcoin Trading?
Trading is the act of buying and selling an asset with the goal of profiting from its price change between the start of the trade and its end. The emphasis here is on Bitcoin’s rise and fall.
Trading is often confused with investing as both involve buying and selling assets. However, they differ in the way they are executed, the time horizon between them, and the mindsets needed to excel at each of them.
Firstly, trading is all about how big price movements are (called volatility). The bigger the movement, the greater the possibility for profit. Traders chase these movements and can profit from swings in both directions.
Investors, on the other hand, do not profit from a decrease in price. While price movements are also important to investors, they only make money when the price of their asset goes up. So they narrow their search to assets that they believe will increase in price.
This difference in focus results in a shift in the qualities both people look for in assets.
Secondly, traders look for qualities like volume and liquidity while investors look for qualities like return on equity and strong cash flow. Traders focus solely on the price action of an asset while investors look at the company, project, or market behind the asset.
For example, a trader may only care about the volume and liquidity of the Bitcoin market while an investor may focus on the level of mainstream adoption, market sentiment, and crypto regulations.
Ultimately, the trader focuses on qualities that affect how Bitcoin trades while the investor focuses on qualities that affect how valuable Bitcoin is perceived.
Thirdly, traders focus on short-medium time frames. A trader never holds on to assets for a long period. Their time frame can be as short as 5 minutes or as long as 1 year, anything longer constitutes an investment. They always close their trades.
Investors, on the other hand, buy to hold for a long period, often multiple years.
Fourthly, because trading doesn’t depend on the intrinsic value of assets, only price movements, traders don’t need to own the assets to profit from their volatility. Financial instruments called derivatives allow traders to profit from price movements without owning the underlying assets.
Investing, on the other hand, involves owning the underlying asset. An investor must buy Bitcoin to profit from it. Hence, a crypto investor will most probably buy crypto from a cryptocurrency exchange while a trader will use a cryptocurrency broker to trade derivatives.
While some crypto exchanges offer derivatives and some brokers, like eToro, also sell cryptocurrencies, the major difference between the two is that the former deals with the real asset while the latter deals with derivatives.
There are three major types of crypto derivatives. They include:
-
CFDs: a Contract for Difference (CFD) is a product that only reflects the ever-changing value of Bitcoin as the underlying asset without the trader needing to buy the digital currency. Buying CFDs when Bitcoin is dipping and selling when its value is high lets the trader profit by pocketing the difference.
-
Futures: Futures are time-bound trades that the investor is obliged to close at a predetermined time. Like CFDs, the price difference can potentially generate profits.
-
Options: Unlike Futures, a trader has the right to close the contract at any time. This can help in profiting when the trader is comfortable with the value increase, or close if the contract is starting to build losses.
Traders can instantly buy and sell these derivatives, allowing for a much faster way to make profits than holding Bitcoin.
Bitcoin Trading vs Investing
Bitcoin Trading
Bitcoin trading involves profiting from Bitcoin’s price movements either by buying and selling the coin itself or using derivatives like CFDs, futures, and options. Brokers that offer these derivatives usually provide leverage facilities.
Leverage is a credit facility that brokers extend to traders to help them increase the size of their position and the potential profit.
Pros of Bitcoin Trading
-
Access to leverage
-
Highly liquid. You can easily open and close trades
-
24/7 trading. Unlike traditional markets, crypto markets are always open
-
Not affected by market direction. You can profit when Bitcoin rises and falls
-
Need to handle Bitcoin directly or manage wallets
-
Major brokers are usually regulated
Cons of Bitcoin Trading
-
Lack of proper regulation
-
Volatility. While volatility can also be an asset, the crypto market is known for violent swings
-
Geographical restrictions. Crypto CFDs are not authorised in certain countries like the UK
Bitcoin Investing
Bitcoin investing involves buying Bitcoin, usually on an exchange, with the goal of profiting from long-term value appreciation.
Pros of Bitcoin Investing
-
Ownership of the underlying asset
-
Ability to use Bitcoin as collateral for loans
-
Potential long term wealth source
-
Total control over asset
Cons of Bitcoin Investing
-
Cannot benefit from price declines
-
Market prone to significant losses
-
Some exchanges aren’t regulated
Where Can I Trade Bitcoin?
Our list of recommended brokers is a good place to start. It is a combination of online brokers and crypto derivative exchanges. Both platforms are suitable for trading Bitcoin and involve similar steps when trading. Nevertheless, they are different and each brings unique benefits to its users.
Some of the Top Platforms for Trading bitcoin
Online Brokers
Brokers are trading platforms that give you the chance to invest when Bitcoin is dipping and then sell off when the value is high. However, traders never buy Bitcoin through online brokers, but contracts that give them the right to their original money plus any profit/loss made when the contract expires or closes. Apart from a few brokers, nearly every trading platform offers the trading of Bitcoin derivatives, which are different contracts that follow the underlying asset (Bitcoin) and have complex rights and obligations from either side.
Benefits of Using a Broker to Trade Bitcoin
-
There’s no need to buy Bitcoins. You can simply buy any of the available contracts and then sell them off when sufficient profits are made.
-
You can determine your level of exposure to the underlying asset and increase profitability through leveraged trading. Some brokers offer as much as 100x leverage.
-
Since Bitcoin is a cost-effective digital asset, traders can start with a very low amount, with some exchanges offering as low as $100 for derivatives.
-
Reputable Bitcoin brokers are compliant with regulatory authorities in the United States, so they offer greater security.
-
With clarity on the different fees they take on bitcoin trading, brokers can be very transparent in their dealing with traders.
-
Brokers also tend to attract experienced traders and offer a variety of trading tools that make it easier to not only make trades but the trading decisions themselves.
Derivative Exchanges
In their infancy, Bitcoin exchanges were simply about buying and selling, offering a very easy onboarding process for people. Over the years trading platforms have started to offer a variety of services, including derivatives. You can now trade on several exchanges without the need to register on a separate broker.
Bitcoin exchanges such as Binance and OKEx are good examples of derivative exchanges. Both offer Futures, Options and leveraged trading (up to 100x).
Benefits of Using an Exchange to Trade Bitcoin
Though the end game of using a broker or a crypto exchange is to trade Bitcoins and generate profits, there are some advantages of using an exchange.
-
Bitcoin exchanges allow for their users to buy Bitcoins and hold the digital coins as opposed to a broker firm in which traders only buy or sell contracts that follow BTC price movements. The users can withdraw their BTC from the exchange at any time.
-
Exchanges have a wider support for deposits and withdrawals with peer-to-peer (p2p) markets often supporting tens of payment methods and fiat currencies.
-
This also translates into a greater selection of bitcoin trading pairs and more flexibility of users to buy or sell Bitcoin against different currencies.
-
Exchanges also offer a much-simplified experience, letting novice users execute trades easier than the complex contracts brokers offer.
-
Many exchanges have also started offering derivatives, including leverages, meaning a user can avail both types of services with one platform.
Beginners Step by Step Tutorial to Trading Bitcoin on eToro
To begin trading Bitcoin, you first need to determine your trading style and strategy. It is advisable to try out a couple styles and strategies first. The results will inform you of your strengths and weaknesses, and you can then determine whether or not you can excelat trading Bitcoin.
Before diving into crypto trading, you should find out how your daily schedule may affect the different trading strategies you may want to use.
For example, if you have a full time job, scalping and day trading may not be ideal as they require all-round vigilance. You’d be much better at swing trading, position trading, or HODLing.
The type of instrument you trade also has a bearing on your strategy. For example, futures contracts usually have expiration dates, so you cannot use the position strategy with them. The same applies to options contracts.
However, instruments like perpetuals do not expire, so they work well with all trading strategies. CFDs do not also expire and are suitable for long term trades. However, they come with overnight fees that could stack up pretty quickly if you are not careful.
Our beginner’s guide focuses on how to start trading Bitcoin CFDs. If your strategy requires holding the actual asset, like the HODL strategy, refer to our Bitcoin buy guide to learn how to buy Bitcoin from a reputable exchange.
To trade Bitcoin CFDs with eToro, follow these steps:
-
Sign up to eToro, upload KYC information (ID card and utility bill) and fund the account with your preferred means, either crypto or fiat.
-
Choose Bitcoin as the asset in the Discover section and click on Trade. An order book and purchase terminal should load.
-
Select sell to short Bitcoin CFD and buy to go long. Shorting means you profit from a price decline while longing means you profit from a price increase.
-
Select leverage (use with caution). Leverage is the borrowing facility that brokers extend to clients. It is a double-edged sword as it greatly magnifies your profit and loss.
-
Choose the amount you want to trade. Note that if you use leverage, the size of the contract will be the amount you choose plus the leverage multiplier.
-
Set a stop loss and take profit, if required. To mitigate possible losses, you can set a stop loss which automatically closes your position if price falls below a certain level in a buy trade. You can also set Take Profits to automatically close your trade and book profits when price rises to a certain level in a buy trade.
-
Open the trade. Once you’ve set your parameters, open the trade. The position remains open until you close manually or either the stop loss or take profit is achieved.
Fundamental vs Technical Analysis - Understanding the Factors That Influence Bitcoin Price
Bitcoin’s price is influenced by several factors that can be categorised in two camps: quantitative factors that deal with price, volume and mathematical elements, and qualitative factors that deal with intrinsic or inborn elements.
To fully understand why Bitcoin’s price moves as it does, you’ll need to analyse these factors. Because they are different in nature, you’ll need two different methods of analysing them, called fundamental analysis to evaluate qualitative factors and technical analysis to evaluate quantitative factors.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis is the study of the underlying factors that make Bitcoin what it is and affect how it is perceived. This includes the blockchain, its developers, its use cases, tokenomics, demand and supply, regulations, and its community.
News
As a global digital asset, a piece of news rising from one part of the world concerning Bitcoin can have an impact on it all over the planet. Visit good crypto news platforms and websites, paying close attention to Bitcoin adoption, regulations, any scams or hacks and in general, any news that can sway investors and traders.
Supply and Demand
Bitcoin is subject to price fluctuation due to varying supply and demand. Though hard-coded to produce 21 million coins in totality, the supply in the trading and exchange market can change as people pour in money or pull out Bitcoins to private wallets.
Follow the general rule: An increase in supply will always put downward pressure on its price, while an increase in demand will push up its price.
Mining Hashrate
Bitcoin uses Proof of Work (PoW) to run complex computations and complete transactions and create new blocks. The more miners compete, the higher the hash rate. A higher hash rate indicates that miners are finding it profitable to run as Bitcoin’s price is increasing.
Tokenomics
Tokenomics is the study of the economics of coins: how the supply, demand, creation, and management of a coin affects the broader crypto ecosystem. Bitcoin has a maximum amount of 21 million, meaning that there will only ever be 21 million Bitcoin in existence.
At the current mining rate, all Bitcoins will be mined in the year 2140, after which no new Bitcoin will exist.
This cap in supply makes Bitcoin a deflationary coin. If demand remains constant after supply runs out, the price of Bitcoin is expected to rise significantly in value. This reality alone makes it valuable in the long-term, if demand remains constant. Tokenomics has significant influence over the present and possible future value of cryptos.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is the study of price action using candlestick charts. It involves observing the relationships between several aspects of price movement like volume, volatility, support and resistance levels, and market structure.
Technical analysts study Bitcoin’s past price movements and, using mathematical formulas, predict how its price will move in the future. These formulas are called indicators.
Some important aspects of technical analysis include:
Candlestick Charts
Candlestick charts are a type of price chart that represent price movement as candlesticks. that are made up of a body and two wicks. The body shows the direction and magnitude of price movement as well as where it opened and closed while the wicks show the highest and lowest points that price reached during a specific time frame.
Market structure
Market structure is the trend of the cryptocurrency markets. Bitcoin’s price can either trend upwards, downward, or sideways. When price trends upwards continuously, the market is said to be bullish. When it trends downwards, the market is said to be bearish, and when it trends sideways, the market is said to be ranging.
However, because the market never moves in a straight line, there are still periods where Bitcoin’s price falls to create a low before moving higher in an uptrend. This action is called a pullback. Successive uptrends and pullbacks cause a wave-like price movement that is used to read the market structure.
Hence, an uptrend is characterised by higher highs where subsequent peaks are higher than their predecessors and higher lows, where subsequent lows are higher than former ones. A downtrend is characterised by lower highs where the subsequent peak is lower than the previous, and lower lows where subsequent lows are lower than the predecessors.
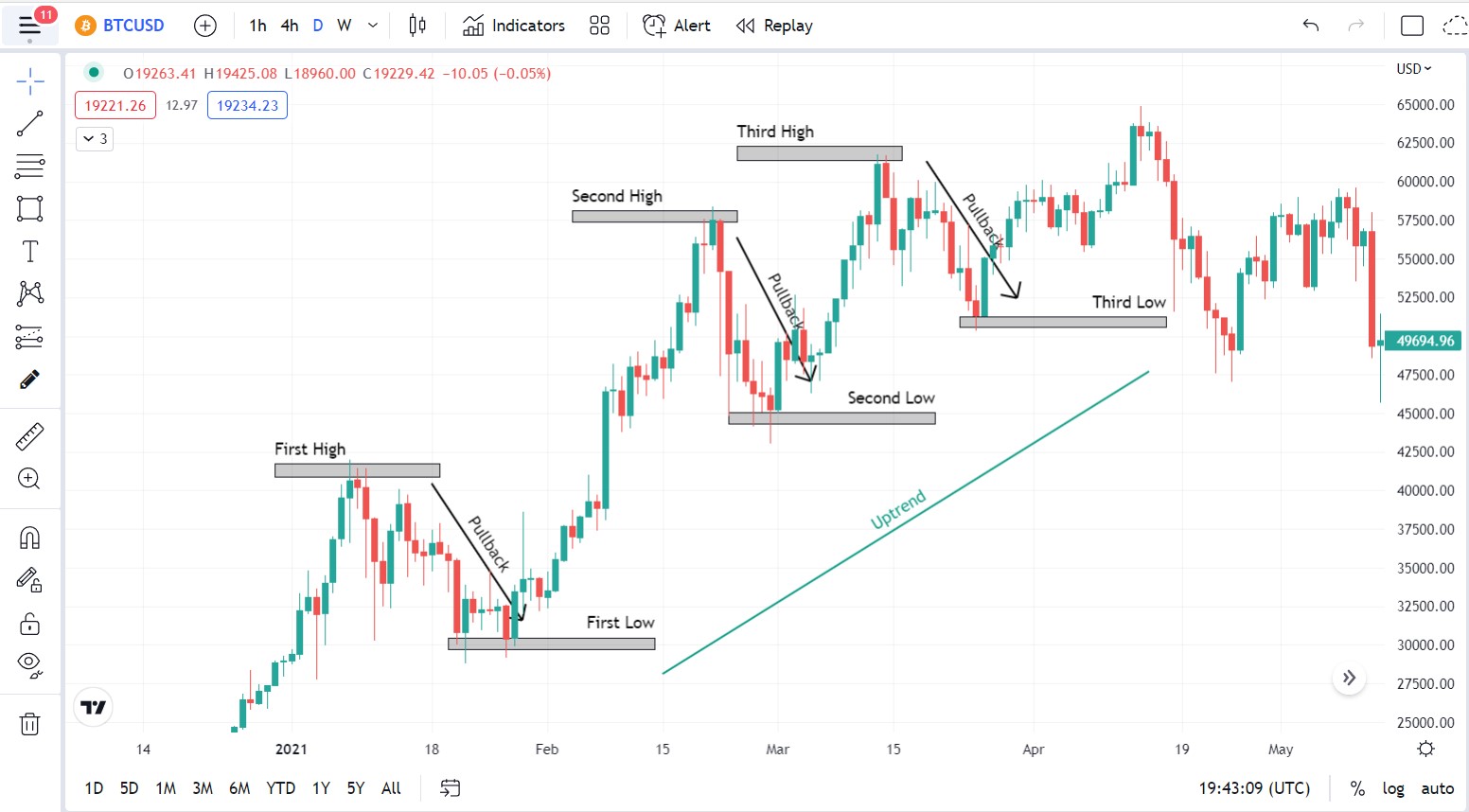
Uptrend is characterised by successive highs and lows where each high and low are above the ones before them.
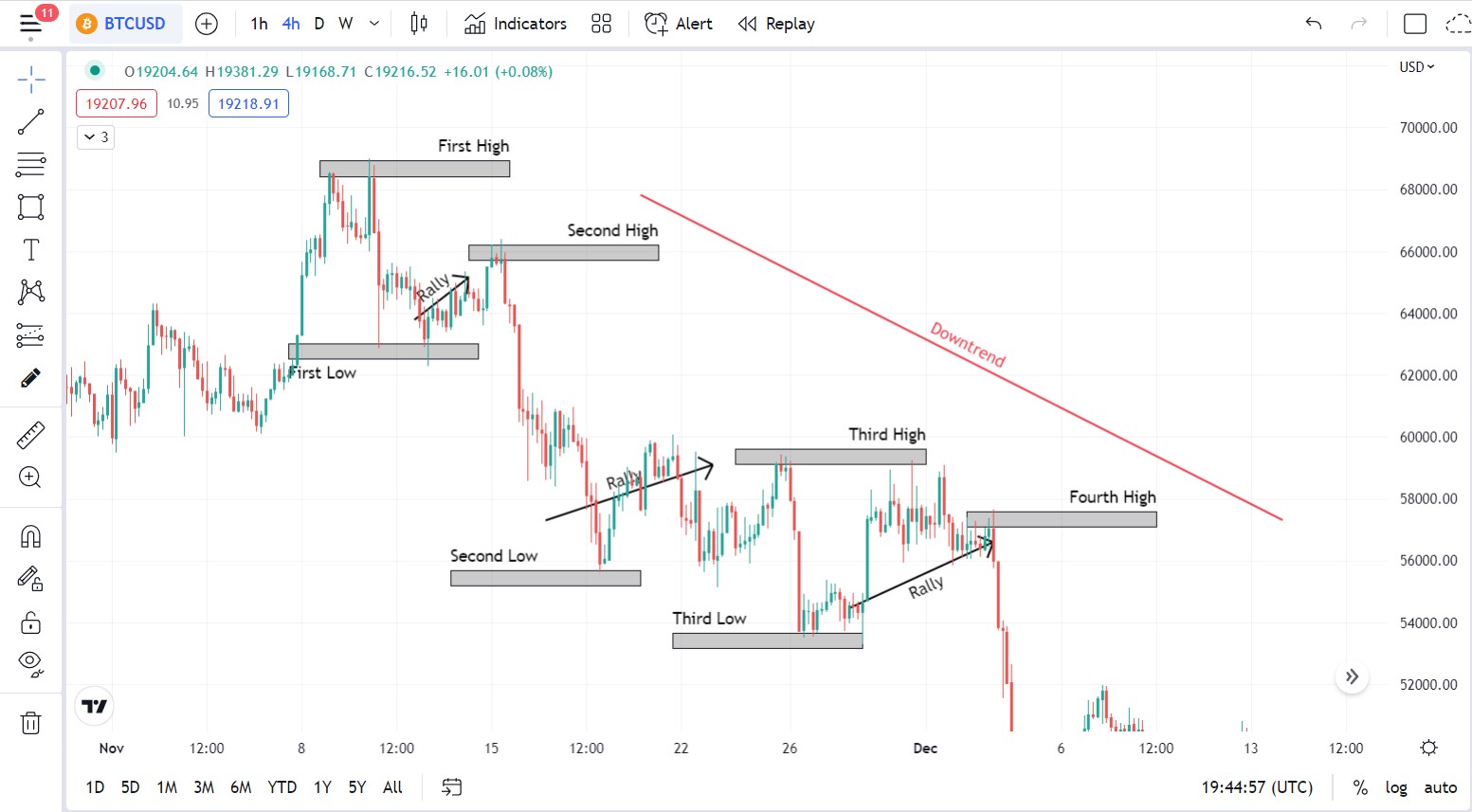
Downtrend characterized by successive highs and lows where each high and low are below the ones before them.
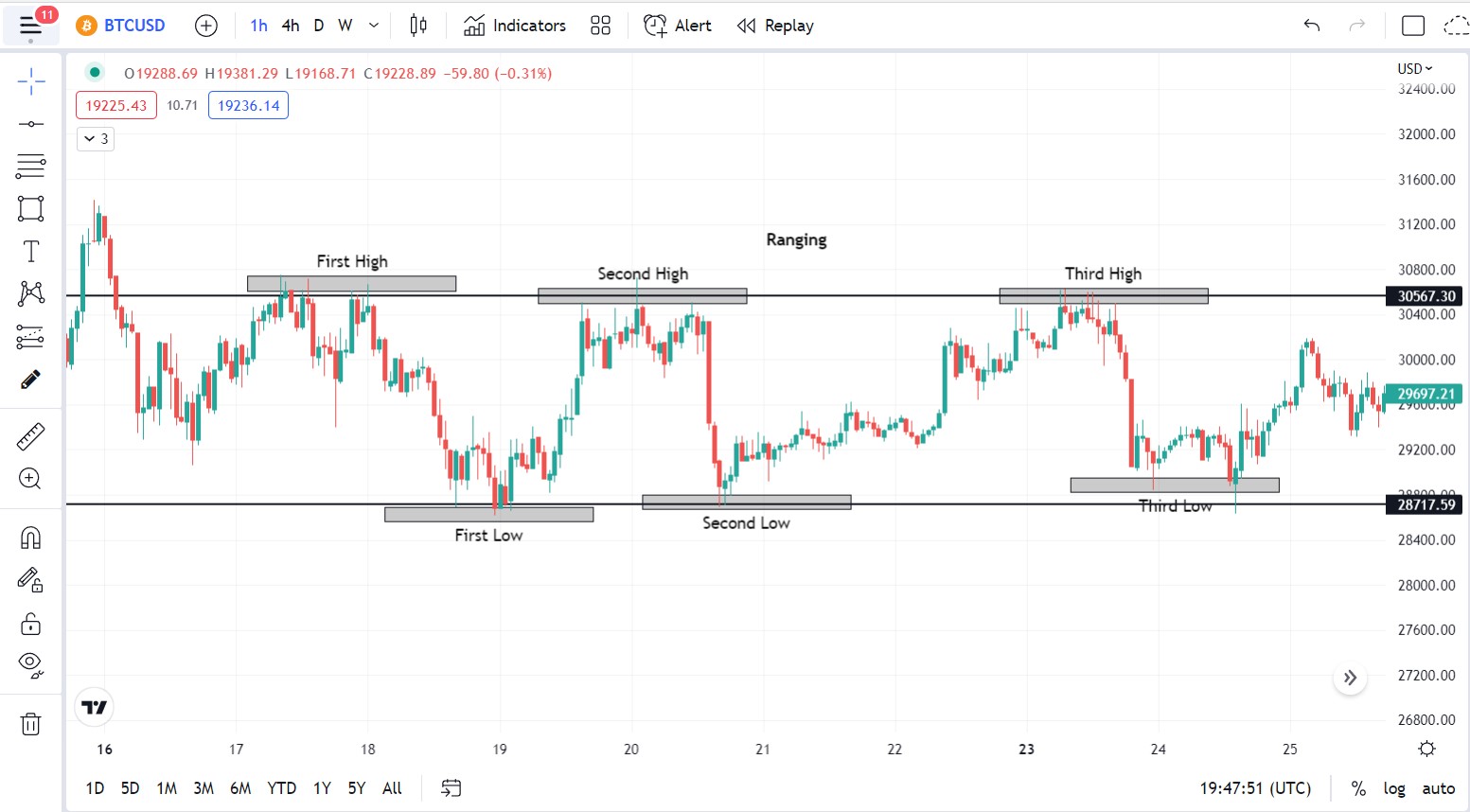
Ranging cryptocurrency markets are characterized by successive highs and lows that are more or less on the same level.
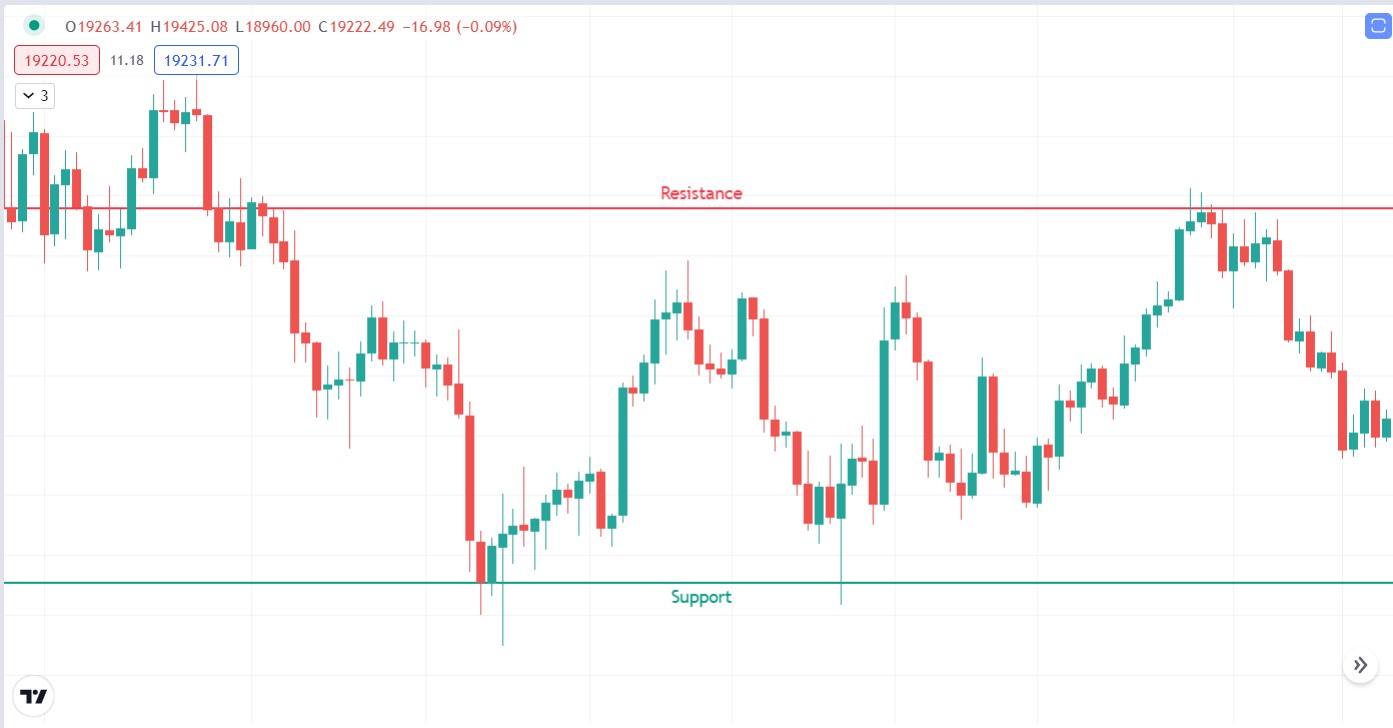
Support and resistance levels
Support and resistance levels are points where price tends to face opposition in its movement. This opposition is due to the activity and sentiments of buyers and sellers.
For example, when the price of Bitcoin decreases, it gets to a point where traders believe it is at a discounted price, so they are willing to buy. This creates demand or a buy pressure that reverses the downtrend, and price begins to go up. The level where demand is the highest and price begins to rise is called a support level.
The same goes for an uptrend. When the price of Bitcoin climbs, it gets to a point where the traders who bought at a lower price may want to cash in on the profit they’ve made. They begin to sell, which creates sell pressure and the price begins to fall. The point where this happens is called the resistance level.
Indicators
Indicators are mathematical formulas that either signal a change in trend or confirm the continuation of the current trend. They are of four types: trend indicators, volume indicators, volatility indicators, and momentum indicators.
Trend indicators confirm the direction the price is currently moving (usually either upward, downward, or sideways) and signals a coming change.
Volume indicators show increases and decreases in the trade volume and usually represent this information as line graphs. A rule of thumb is that significant volume increases usually signal major price movements.
Momentum indicators measure the strength of price movements. They are called oscillators because they represent data on a scale from 0 to 100 and fluctuate within the range. For example, if Bitcoin’s price is rising quickly, the momentum indicator will show strong upward movement, and when price begins to fall, the indicator falls. A rule of thumb is that momentum movements precedes price movements. So momentum indicators signal which direction price will move next.
Volatility indicators show the erraticness of price movements. On some days, Bitcoin’s price moves quickly, on other days it moves slowly. The emphasis is not on the speed of movement but how far price moves within a specific time, called price swings. Volatility indicators measure the strength of these swings.
While hundreds of technical indicators exist in these four categories, most traders use only a few. The most common ones used are:
-
Moving Averages: Bitcoin’s moving average is the average of its closing price over a specified period (e.g. 50 days or 50 hours). The simple moving average (SMA) shows the current price trend. Variations of the SMA also exist like the Exponential moving average (EMA) which emphasises the most recent price movement.
-
Relative Strength Index: The relative strength index (RSI) measures how strong recent price movements are the magnitude of price and represents that information on a scale between 0 and 100. It is a momentum indicator
-
Moving Average Convergence Divergence: The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is the difference between the 26-day and 12-day EMA. The result is plotted against a 9-day EMA line, called a “signal line”. MACD is a combination of a trend indicator and a momentum indicator that shows both price trend and momentum. Upward MACD movement signals upward price movement.
-
Bollinger bands: Bollinger Bands is an indicator that shows the volatility of Bitcoin’s price as a channel around price candlesticks. The more volatile the market, the wider the channel.
You can learn about several other popular indicators like Fibonacci Retracements, Stochastic Oscillators, Money Flow Index, and Ichimoku cloud.
What causes Bitcoin’s price to fluctuate?
Bitcoin’s price is affected by several market factors:
-
Sudden increase in demand or supply
-
Market cycles. The crypto market has a four year cycle, usually two bullish years followed by two bearish years.
-
Psychological support and resistance levels. Institutions usually have prices that they believe are good levels to buy and sell. When price reaches those levels, there will usually be a reversal as traders execute their buy/sell strategies
-
Mainstream acceptance. As more stores, lending institutions, etc, accept Bitcoin, its price increases.
-
Regulations. News of Bitcoin being legal in a major country would give the coin more legitimacy and result in an increase in perceived value, ergo price.
Methods of Trading Bitcoin - What Trading Strategies Can I Use?
While the ultimate goal of trading Bitcoin is to generate profit, Though you, like every trader, will have only one goal in Bitcoin trading: making a profit, the essential thing to consider here is how to achieve it. There are several trading strategies that you can employ:
HODL
HODL, often translated to mean Hold On for Dear Life, originated in the crypto industry as a typo of the word Hold which means to not sell your coins even in bear markets. Hodling is geared more towards investing than trading as it requires investors to refrain from selling, and traders always sell.
However, to increase this strategy’s effectiveness, you can buy more Bitcoin when the market is down and sell when it gets to a peak, but you must buy it back when the price falls. Judging from Bitcoin’s price history over the last 7 years, holding is a good strategy, albeit one that requires time and patience.
Day Trading
Day trading involves opening and closing trades within a day. This strategy capitalizes on Bitcoin’s volatility to turn a profit. The more volatile the price, the higher the profit (and loss) potential.
Day traders usually stick to the 1-hour time frame to capture small price movements. They could open multiple trades to capture several tiny profit margins that add up to a more tangible overall profit margin.
Day traders may also use the news trading strategy where they try to predict the outcome of an important news announcement and open trading positions beforehand. A good example is shorting Bitcoin when the government is about to announce a significant hike in interest rates.
Ultimately, day trading requires skill and patience and is not usually recommended to newbies.
Swing Trading
Swing trading is a strategy that capitalizes on price swings. A price swing is a significant change in the price of a security, and the swing strategy involves anticipating this change and opening a trade in the same direction before that change happens.
Swing traders look for swing highs and swing lows as critical starting points for their trades. A swing high is the most recent peak reached within a specified period and is confirmed by a lower peak before it and a lower peak after it.
So also, a swing low is the lowest point reached within a specific time frame and is confirmed by a higher low before it and another higher low after it.
Traders buy at swing lows and sell at swing highs. Depending on the time frame used, swing trading could take days, weeks, or even months.
Hedging
Hedging is not exactly a trading strategy. Instead, it is a risk management technique that helps traders offset their risk in a particular position by opening a trade in the opposite direction of the related asset.
For example, a trader who owns Bitcoin can hedge against the risk of a price crash by buying a short futures contract of the same value. If the price of Bitcoin falls, the value of the coins drops, but the same value is gained by the futures contract so that ultimately, the loss from the coins is negated by the gains from the futures.
This way, traders and investors protect against risk from volatile swings. Hedging works well for investors with significant Bitcoin holdings, but can also be adopted by traders.
Scalping
Scalping works similar to day trading but on a much smaller time scale, from a few seconds to minutes, with very small profits being made. However, the sheer number of trades executed can add up to significant profits if done properly.
Scalpers stick to ultra small time frames, usually from a few seconds to 30 minutes when scalping, and open numerous trades.
Position Trading
The position trading strategy involves capitalizing on major market movements that could take days, weeks, months and sometimes even years. This trading strategy often resembles investing except that it also includes financial derivatives.
Some minor trading strategies include copy trading, trend trading, end-of-day trading, and news trading. Each carries its benefits and drawbacks. In the end, it is you who has to decide which one is the best and then stick to it.
Important Bitcoin Trading Terminology & Tips
Trading literature is littered with jargon and industry-speak that newbies may not understand. So here are some important trading terminologies.
Short or Long Positions?
If you believe that the price of Bitcoin is set to rise, you can open a long position. This essentially means you will open a Bitcoin contract at a specific price and then close it at a higher price, making profits.
On the other hand, if you believe Bitcoin’s price will fall, you can still profit by opening a short position. You essentially borrow Bitcoin from a broker, immediately sell it, and wait for the price to fall.
When the price falls, you buy back the same amount of Bitcoin but at a lower price so it doesn’t cost as much to buy it back. After returning the borrowed Bitcoin to the broker, the leftover cash from when you first sold the Bitcoin is your profit
However, with CFDs, you don’t need to borrow actual Bitcoin since the contract is an agreement to exchange the difference in price of Bitcoin from when the contract is opened to when it is closed.
Shorting is generally riskier than longing because an asset’s value cannot fall below zero, so a long trade that goes bad has a limit to the losses it can incur. However, an asset’s price can theoretically rise forever. So a short trade gone bad could lead to unlimited losses.
Limit or Market Order
A Market Order is an instruction to buy an asset at its current market price. You cannot set a preferred price when using market orders as your broker will execute the order immediately at the most recent price set by demand and supply forces. You can only set the quantity you wish to buy.
If you wish to buy Bitcoin at a price lower or higher than its current price, you’ll need a limit order. This order instructs your broker to buy BTC at your desired price. When setting the order, you enter your desired price and the amount of BTC you want.
When Bitcoin’s price falls (or rises) to that level, your broker will execute the order. In the meantime, you wait.
Limit orders can help you buy in at favorable prices, however when analysis is not properly done, you could place your limit price too low and miss a good opportunity.
Trade Position Amount and Leverage
Your trade position amount is what you place in the order. Many platforms give another edge to users by offering leverage. This allows traders to gain more exposure to the market by placing less than the actual amount in the trade. Brokers lend money to their users in this case.
Trading platforms define the margin requirements and display it in ratios, such as 10:1. This means that by holding $1,000, you can open a $10,000 Bitcoin trade. The increased exposure translates into higher profits, but the pendulum can swing both ways, meaning losses are also amplified.
Risk Management: Deciding the Right Stop-Loss and Take Profit values for Your Bitcoin Trade
Stop-Loss orders are employed to mitigate losses as the market turns red. Placing two key input Bitcoin values determine when the order is triggered: the Stop Price (defined market rate) and the Limit (price you want to be sold in the market once triggered).
Using your analysis, you can place the Stop-Loss orders just below key support levels, where you are sure that the market will bounce back. In case Bitcoin value keeps dropping and crosses the support level, the order will be triggered and your positions closed, saving your losses.
Trailing Stop-Loss orders is a variation in which the order continues to adjust to the changing floor resistance levels as the market goes up. Should Bitcoin fall below the latest support level, the order would trigger.
Trailing Stop-Loss orders allow traders to continually move their closing positions to mitigate losses while allowing them to make as much profit as possible.
Stop-Loss and Trailing Stop-Loss orders can be useful for traders who aren’t very active; if the bitcoin market goes down, they can automatically pull out without needing to log onto their trading account.
How to Read a Bitcoin Price Chart
A Bitcoin price chart used by traders will most likely look like this:
This is the candlestick chart talked about earlier. The red candles signify price falls while the green represent price rises. Each candle represents a time period. For the chart above, each candle represents one day.
The bottom of the green candles are where Bitcoin’s price opened for that day and the top is where price closed. Candles that have a thin line stretching from either the top or the bottom show the highest and lowest point that Bitcoin’s price reached that day.
Notice how several candles placed together show a trend over several days that are composed of both red and green candles. This is how trends work. While there may be positive and negative days, price will move in the direction of the overall trend in the long run.
Some traders prefer to use line charts. Line charts show the overall trend of the market but do not offer extra information like the open price and the highest and lowest price.
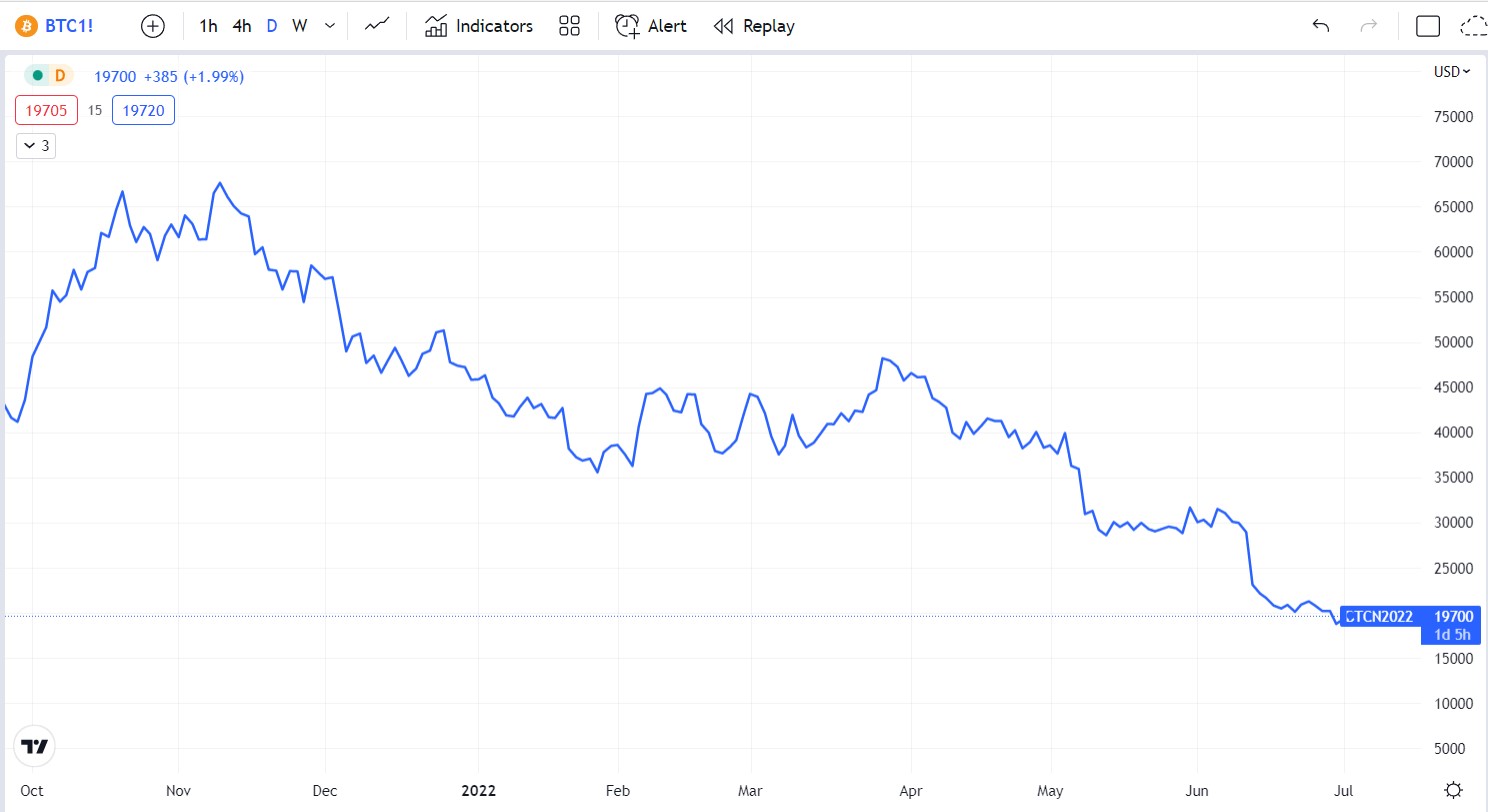
The line chart above clearly shows Bitcoin’s trend, but not much else.
A consistent downward price movement, like the one displayed above, is called a downtrend. If the line was in an upward direction, it would be an uptrend. Traders look for selling/shorting opportunities in downtrends and buying opportunities in uptrends.
Practice Trading Bitcoin
You can practice trading before trying with real money. Brokers like eToro provide demo accounts for newbies to practice with. You trade with real market data in a real market scenario but without real cash. This is often called paper trading.
Experienced traders also use demo accounts to try out new strategies, learn new techniques, and perfect their plans before live trading. Newbies can use demo accounts to test the waters. If they believe they can swim, they may move to a live account and trade with real money.
What to Watch Out for When Trading Bitcoin
Overtrading: Overtrading is the superfluous trading of securities. Opening too many trades in a bid to maximize profit will end up doing the exact opposite, losing money. Individuals usually have a psychological limit beyond which trading in a limited time period becomes counterproductive. Instead of opening many trades, focus on opening a few well planned ones.
Too much leverage: Leverage is a way to increase potential profit, when used properly. When used carelessly, it can wipe out your entire trading account. In fact, brokers in certain regions are not legally allowed to offer leverage facilities beyond a certain limit. Countries like the US limit brokers’ leverage to 50:1.
Volatility: Volatility is the degree of erratic-ness of price represented by how large the price change is within a time frame. Volatile markets are good for making profit quickly, but they cost you just as much just as fast. Trade volatile markets with caution.
Unregulated platforms: Unregulated platforms are not beholden to any regulatory agency. This means that the safety of clients’ funds is at the discretion of the broker. It’s best to stay away from unregulated brokers.
Market manipulation: Market manipulation happens when one or more players with large enough volume artificially moves the market in their favor, usually to the detriment of others.
Changes in patterns: A change in pattern is a shift in the current market trend, behavior, or structure. Usually, the market starts moving in the opposite direction.
Over exposure: Overexposure occurs when a trader invests too much capital in one trade/asset or in the market altogether. There could be too much capital in the same industry or type of asset in a way that a fall in the value of that asset places a significant chunk of capital at risk.
Marrying your bags: Marrying your bags is an unwillingness to close a losing trade because of sentimental reasons. Either because you “believe” in the asset or are unwilling to let go of the losses you have already incurred.
Diversification: Diversification is the act of varying your portfolio by investing in different types of assets or assets in different industries. The goal is to spread your risk by investing in a basket of assets that are not all correlated. Market conditions that may not be favorable for asset A may be great for asset B. If you have both assets in your portfolio, you can offset losses made from asset A by profits gained from asset B.
Overdiversification: Overdiversification occurs when you spread your portfolio too thin by investing in too many assets. The result is that gains made is negligible as the capital invested in each asset is too small for the profits to count.
Scammers: Scammers are people or organizations that promise profits that are too good to be true. Their goal is to goal naive newbies into giving them money or paying for courses that do not provide value.
Choosing a Bitcoin Wallet for Trading
If you plan to use the HODL strategy or trade using actual Bitcoin (and not a contract), you’ll need a wallet. There are different types of wallets suitable for various traders depending on the level of security they want, their trading frequency, their broker/exchange, and their trading strategy.
Wallets are categorized into two main categories: hot wallets and cold wallets.
A hot wallet is one that is constantly connected to the internet. It is usually a software wallet, called a soft wallet, like a browser wallet, desktop wallet, crypto exchange wallets, or mobile app that stores private keys on the device it’s on.
A cold wallet, on the other hand, is one that is not connected to the internet. This wallet keeps your crypto and private keys offline. This type of wallet includes hard wallets like the Ledger Nano S.
If you wish to trade crypto frequently, you’ll need a hot wallet, preferably an exchange account. Brokers like eToro also provide exchange wallets for users to store coins and trade at any time.
Hard wallets are better for long term strategies like position trading or the HODL strategy as coins are stored offline for long periods.
Our Bitcoin wallet page further breaks down the differences between hot and cold wallets and even explores further subcategories like mobile and desktop wallets.
Final Thoughts
Trading Bitcoin is different from investing in a number of ways. Firstly traders focus on profiting from Bitcoin’s price movements while investors look to profit from long-term price appreciation.
Secondly, traders use derivatives like CFDs, options, and futures to profit from price movements while investors stick to buying the underlying asset. And lastly, traders always sell while investors may hold on to an asset for life.
To begin trading, you need to be able to combine both technical and fundamental analysis which involves knowing what makes Bitcoin what it is and how the crypto’s price pattern looks.
We focused on Bitcoin CFDs in this article as they are easy to understand and do not have an expiry date. To trade CFDs, you’ll need a broker. We recommend eToro as they have 25 million users, helpful features for newbies, and 75 available cryptos to trade, including Bitcoin.
To begin using eToro to trade, refer to our step-by-step trading instructions on this page. You can also open a demo account to test the waters without using real money before diving in.
Before trading, ensure you know what strategy works well with your daily schedule (HODL, day trading, swing trading, scalping, or position trading) and what instruments it supports (coin, options, CFDs, or futures).
Learn the trading lingo so you can follow along with popular literature and helpful material. And finally, watch out for pitfalls like spreading your capital too thin by opening too many trades, putting all your funds in one trade, using too much leverage, hanging on to a trade even when it’s a loss, getting emotional when trading, and not using stop loss.
