How to Mine Litecoin in 2025 - Complete Guide
Cryptocurrencies are based on the concept of decentralization, and that means there is no single authority that produces and issues coins. Issuance is achieved by solving complex cryptographic calculations, each successful answer resulting in the solver adding a block to the chain and receiving newly minted coins as a reward.
This is called Proof of Work (PoW), and miners can either do it solo or join a group of other miners to pool their computing power.
If you are interested in mining Litecoin (LTC), read on and learn how to become a miner yourself.
What is Litecoin Mining?
Let’s get down to understanding mining in a bit of detail. After reading this, you will have a clear understanding of what it is, and you can get started with mining Litecoin.
In traditional monetary systems, the creation and issuance of newly minted money and bills are controlled through a central authority, referred to as Central Banks. The transmission is controlled through other banks, which note down the transactions in their ledgers. Litecoin, as a decentralized cryptocurrency, does away with the centralized authorities and uses miners to run the ledgers, transactions, and the creation of new coins.
Using PoW, Litecoin allows anyone to solve complex mathematical problems to note down the transactions made by users and create new blocks. In this process, anyone who solves the problem receives a block reward of newly minted LTC. The problems are solved with computers, and as such, the energy and time spent are a testament to the efforts of the miner; therefore, this process is called Proof of Work (PoW).
Why Litecoin Miners are Important?
Miners are the backbone of any blockchain network and as such, they are the ones that not only secure the Litecoin network but are also progressing the chain. They confirm all transactions through PoW and therefore ensure that double spending is not possible.
Since there are a lot of miners vying to be the first to solve the cryptography and create a block, more than one can achieve it in a given time. This means that more than one miner can add the same block and that would lead to more than one recording of LTC transactions, or double-spending. To solve this, each batch of the transaction is time-stamped before being broadcasted on the network for other miners to update their ledgers.
This creates an immutable record, showing that the transactions are already done, and another block should not contain these. If this happens, the network automatically rejects the transactions and blocks, thereby ensuring that there is only one chain and the whole ecosystem is secured against fraudulent transactions.
Since LTC works on the PoW principle, the miners have to expend a lot of energy running their computers to solve mathematical problems. They are compensated through the block rewards, serving both as a means of paying for their efforts and incentivizing them to keep running the mining operations for network integrity and to guard against illegitimate entries.
The more miners there are, the more secure the network. At the same time, the hashrate increases, and so does the competition to solve the cryptographic problems first, requiring more and more energy leading to more decentralization.
Litecoin Mining Limitations
An early fork of Bitcoin, Litecoin still works on the deflationary principle (albeit with a higher limit of 84 million coins that can ever be created) and a faster block time of 2.5 minutes in comparison to the 10 minute average of BTC. The limited amount of LTC is a crucial factor.
Unlike fiat currency, where central banks can print and issue as many bills as they prefer and create devaluation of the currency, the limited numbers of LTC mean that over time as demand increases, the simple rule of economics comes into play (supply vs demand), thereby ensuring deflation.
At the same time as demand increases, Litecoin supply also dwindles. Every miner who successfully solves the equation and creates a block is given a block reward in the shape of new LTC tokens. Initially, the reward was 50 LTC per block, but using the halving concept, the reward keeps dropping after every 840,000 blocks (taking roughly four years).
The rewards will keep halving, reducing the input of available LTC in circulation until the rewards finally fall down to zero by 2142. Currently, the block reward is set at 12.5 LTC and the next halving is scheduled for a little over 2 years from now.
As more miners join the network, they can solve the problems faster, and that can speed up the issuance of rewards. To counter this, LTC uses an adjustable mining difficulty that increases the complexity of the calculations as more computing power (or hashpower) joins the network. The difficulty adapts to ensure that the block creation time remains consistent at 2.5 minutes. Conversely, if miners move out, the difficulty will fall to maintain the block speed.
Tip to Mine Litecoin Efficiently for Greater Profits
In its initial years, mining was profitable by using normal computers. Today, the hash power has increased to a level where it is no longer profitable to use normal computers. The most efficient way is to use dedicated mining hardware either as a standalone project, join a mining pool, or go for cloud mining. For solo and pool mining, consider the cost of electricity, and if you choose to use cloud mining, the reliability of the service providers and the agreement clauses (reward distribution, profitability calculations, minimum payouts, fees and charges).
Technical Aspects of Mining Litecoin Explained
To truly understand and evaluate mining options, you will need to understand a few technical details and factors involved in the process. The foremost is the hashrate, which determines the difficulty of the network, protects its integrity, and secures it against attacks and hacks.
Hashrate Simplified for Litecoin
-
What is hashrate?
In broad terms, hashrate is the number of calculations a computer or a miner can make in a given time in an attempt to solve the cryptographic calculations and is a good measure of the total computing power dedicated to Litecoin mining.
-
Why is Hashrate Important?
Hashrate defines how much computing power there is on a network. A higher hashrate means more competition and the difficulty of calculations increases. The hashrate also shows how secure the network is, since 51% of the hashrate is needed to hijack the network and a higher rate makes it more difficult. The more power required to attack the network, the more resources the attacker requires.
-
How is Hashrate Measured?
Hashrates are measured in hashes per second, using metric prefixes. LTC is currently using roughly 300 Th/s, meaning 300 trillion hashes per second are being calculated on the network. The hashrate is very important for mining as computers have only limited power and if the network hashrate is too high, your intended computer or hardware setup may not be able to compete.
With the current LTC rate, it is unfeasible to use PCs or laptops, and even for dedicated hardware such as an ASIC, you will need a very powerful one to be able to earn a block reward.
Processing Power: CPU & GPU
As described before, each hardware solution has its limitations of hashrate. Initially, LTC’s hashrate was very low, allowing normal computers and laptops to use their CPUs. Even though Litecoin uses the Scrypt hash function instead of the power-hungry SHA-256 of its parent Bitcoin, people were quick to realize that GPUs, or graphic cards, offered much higher rates, and miners quickly shifted over, making CPU mining obsolete.
Eventually, miners migrated from GPUs to Field Programmable Gate Arrays; these are modular integrated circuits that can be configured to run specific tasks. Miners programmed FPGAs and fine-tuned them towards their required hashpower.
Today, these have evolved into ASICs (Application Specific Integrated Circuits), pieces of dedicated hardware that are created with only one task: to mine. Litecoin ASICs are configured specifically for the crypto, ready to be plugged into a power source and connected to the network (or a mining pool).
Since the mining rigs today consume a lot of electrical power, this has raised another issue: the heat. Computing generates a lot of heat, and a significant portion of the power used to run the mining rigs is spent on the cooling systems, raising questions about mining profitability. Mining farms, in order to be feasible, not only located in areas where electricity is cheap, but the weather and storage ventilation also come into play.
Hashrate Needed to Mine Litecoin Profitably
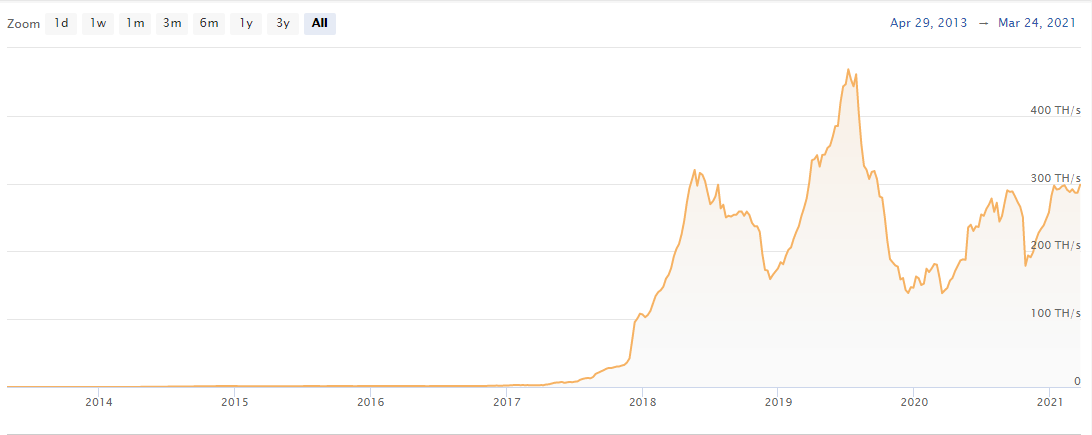
Source: CoinWarz.com
Litecoin currently is using around 300 Th/s (terahashes per second) of computing power. This means that the only option today to mine LTC profitability is to use ASICs, especially the more powerful ones like Antminer’s L3 and its more powerful cousin, the L3+. You might want to check with a Litecoin profitability calculator before investing in mining equipment.
Pros and Cons of Mining Litecoin
Pros
- Earn LTC for securing the network
- Play your part in the decentralised revolution by verifying transactions on the network (and earn transaction fees in the process)
- Cheaper electrical sources can significantly increase profitability
- Contribute to the security of the network
- Mining hardware has a good resale market, letting you recover your invested amount easily
Cons
- Mining rigs are a heavy initial investment
- More powerful miners and pools can lead to reduced chances of successful block rewards
- Energy-intensive machines mean running costs are high
- LTC volatility might lead to losses as more energy will be consumed for lower-priced coins
How to Get Started With Litecoin Mining
If you are interested in mining your own LTC, this section will guide you on how to set it all up yourself, exploring the software and hardware requirements and what expenses you will incur.
Best Mining Hardware for Litecoin
Mining Litecoin is not a feasible option unless you are planning to go big, something like a mining farm with arrays of mining rigs connected in tandem, working together towards finalizing a block. You can, however, invest in some good mining machines and connect with a mining pool. The game is simple: more mining power (hashes per second) means a greater chance. Following are a few of the most popular miners you might want to consider.
The FutureBit Apollo Pod is a good option as a Litecoin starter pack. Though not as powerful as the big machines, it does a good job due to its lower energy consumption. The miner comes in a small stand-alone pod concept (hence the Pod in the name).
The Apollo Pod can give up to 135 Mh/s consuming 1 watt per Mh in economy mode and 1.4 watts in its turbo mode. The device comes with a 64 GB USB drive that is preloaded with the LTC blockchain, helping you spend less time on the first-time synchronization and jump to mining. The Pod is available to order directly from the FutureBit website, costing $320 (plus $15 if you want the SD card).
The AntMiner L3+ is a good option, with it consuming just a tad more than Apollo at 1.6 W/Mh of energy but performing up to 504 Mh/s of computation. It consumes overall 800 watts and comes with a dual cooling fan system to dissipate the extra heat it generates. It is available on Amazon, costing $700, and comes with its own power supply. Don’t be fooled by the low price, though. The L3+ is out of production, and only models used are available, hence the low price tag.
If you want to go all-in on mining LTC, you should check out the Innosilicon A6+ LTC Master. This beast is one of the most powerful LTC mining ASICs in the industry, churning out 2.2 Gh/s. The high power comes at a cost, though, consuming 2.2kWh of energy.
The popularity has led to all units being sold out at the moment, and you will need to get in line for the opportunity to get your hands on it. Priced at $3,000 a unit, it will set you back a whopping $30,000, as a minimum of 10 units can be ordered.
Other Costs to be Considered for Mining Litecoin
Though the machine manufacturers declare the costs of the ASICs, other factors come into play. You will need a computer too that you must hook up with the miner to configure and run.
Your location is also important. Different locations and electricity suppliers have their own rates and that can change the cost of running the machines. If you are located in a temperate or hot climate zone, you will need to additionally invest in cooling apparatus. If you intend to join a mining pool, they will have their charges and the block reward distribution policy.
Mining Solutions/Services
If you don’t want to go through the hassle of buying and setting up your rig, a cloud mining solution is your best option. Basically, you rent out the ASIC power of another user, sharing the rewards. Though easier, this option has to be carefully considered.
The key to selecting a cloud mining platform is to read the fine print in the agreements, along with any mention of guaranteed earnings, contract length, maintenance costs, and the cost point where they can dissolve your account. Scammers are common in the cloud mining space, so always do due diligence when researching platforms, and remember: if it seems too good to be true, it probably is.
CCG is one of the most popular legitimate cloud mining contract providers. It provides the highest hashrate and offers a choice of contracts to suit different aims and budgets.
A thorough cost-benefit analysis is a good way to find out if it is worth buying your own ASICs or investing in cloud mining. Where owning a machine means a significant startup investment, the main cost comes in running the machines and their cooling requirements. Cloud mining frees you from these, and the rent is low but can amount to a lot of money if you are not actually earning any rewards.
If you buy your own equipment, mining pools are a logical option for individual miners since the hashpower of Litecoin currently means that it is nearly impossible to be in profit unless you shell out a huge amount of money for a collection of the top-of-line ASICs. You can buy a cheaper mining machine and join one of the many pools that work as a distributed computing network, combining power and working in unison to find blocks.
Different mining pools have their own method of determining how you are rewarded. The simplest method is Pay Per Share, which guarantees you LTC payouts, even if the block is not successfully mined. Your payout depends on your hashrate contribution to the total pool size.
Full Pay Per Share is a variation where pool contributors are also given a share of the transaction fee earned. Pay Per Shares are the most complex reward system and runs higher risks. You are paid LTC only if the pool manages to mine a block successfully. In order to compensate for the increased risks, users are rewarded much higher than the other options.
Once you have decided on which mining pool you want to join, you can simply set up your ASIC, download and install the necessary software, and connect to the pool.
Start Mining Litecoin
Now that you are all ready to buy the ASIC you want, you can set it up and mine. But first, there are a couple of other things you need to ensure.
You will need to install the relevant ASIC software, which will communicate with the Litecoin network. Furthermore, a Litecoin wallet will let you store your earned coins.
Easy Miner is the most appreciated mining software available for LTC. It is open source and can be configured for a variety of devices. CGMiner is another good choice but since it is a command-line version, it is not for people who are used to graphics-based user interfaces.
Awesome Miner is fine-tuned towards managing multiple rigs and if you are running your own large array, consider this.
Mining pools are the best option if you are on a budget. A mining pool works by combining the hashpower of multiple miners and sharing the block rewards between participants. This gives miners a much more consistent stream of income.
Before committing to a pool, be sure to check out the reputation and their past performances. A larger pool is likely to get more hits on block rewards, but this also means the payouts are diluted. LTC.top leads the pack with 22% of all hashpower. AntPool from BitMain is another popular choice. Other major pools include F2pool and LitecoinPool.
Where to Save My Coins After Mining?
Wallets, of course! The selection of the cryptocurrency wallet, however, depends on you. If long-term storage is your aim, go for a paper or a hardware wallet. If you want to actively trade or liquidate your earnings, you can use a software wallet to manage your funds more conveniently.
Your wallet is perhaps the most crucial part of securing the coins you have worked so hard to mine. For your ease, we have listed the best LTC wallets below.
Alternatives to Litecoin Mining
Mining isn’t for everyone—acquiring the right hardware and powering it can involve a significant amount of effort and expense. What’s more, you may find yourself competing with industrial-scale mining operations, such as Riot Blockchain, Marathon Digital Holdings, and Argo Blockchain.
A simpler and cheaper way to profit from mining is to buy shares in one of these mining companies. This is easily done by signing up with a broker that offers mining company stocks. You can get started by clicking on the link to our preferred partner below.
Riot Blockchain (RIOT)
Riot Blockchain has Bitcoin mining facilities in New York and Texas, including North America’s single largest Bitcoin mining and hosting facility. The company aims to increase its capacity and hash rate by expanding its operations with the purchase of more mining machines.
Marathon Digital Holdings (MARA)
Digital asset technology company Marathon Digital Holdings has been around since 2010, when it started collecting encryption-related patents. The company already has a sizeable fleet of Bitcoin miners and aims to build North America’s largest mining operation while keeping energy costs low.
Argo Blockchain (ARB)
Argo Blockchain comprises a dynamic team of mining and blockchain experts that prize innovation. The company supports the development of blockchain technologies and advocates the use of renewable power sources to create a sustainable blockchain infrastructure.
